WASHINGTON: An Afghan campaigner who took part in breakthrough talks with the Taliban said Thursday she saw subtle improvements in the attitude towards women of the insurgents, who severely curtailed their rights while in power.
In a meeting in Qatar, earlier this week, the militants sat down with Afghan representatives and issued a joint statement that called for assuring women’s rights “within the Islamic framework of Islamic values”.
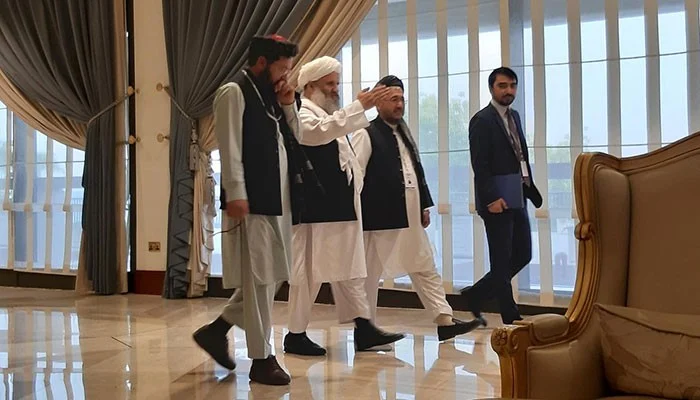

The conference, co-organized by Germany, came as the United States negotiates with the Taliban to pull troops from Afghanistan — with women’s rights not explicitly on the agenda.
Asila Wardak, a women’s rights campaigner who works for the Afghan foreign ministry, said she was surprised at the positive atmosphere in Doha as women mingled directly with the Taliban over dinner and tea breaks.
“It was interesting to me as an Afghan woman as they didn’t shake hands but they warmly welcomed us,” she told a symposium at Georgetown University on the peace process, speaking by video from Kabul.
Two Taliban delegates even showed flashes of humour, telling the Afghan women that they heard they would be coming and saying, “‘Please don’t give us a hard time,’” she said.
“Maybe I’m wrong but their attitude has totally changed towards women, towards government employees,” she said.
“But I do not say that their behaviour (changed) or, ideologically or strategically, they didn’t change anything,” she said, pointing to a massive blast in eastern Afghanistan that killed 12 and injured dozens of children just as the Qatar talks were opening.
Ghizaal Haress, a constitutional scholar at the American University of Afghanistan, said it remained unclear what the Taliban were saying by signing the declaration in Doha.
“The term ‘Islamic regime’ is very vague, it’s very broad and there is a fear of what it will mean under the interpretation of the Taliban,” she said.
“Do we mean an Islamic regime like the one in Malaysia or Indonesia? Do we mean an Islamic regime like Saudi Arabia or Iran? Or do we mean one like Pakistan?” she said, referring to governments with varying degrees of openness toward women.
The Taliban were notorious for their harsh treatment of women during their five-year rule of Afghanistan, which ended with the US-led invasion after the 9/11 attacks.
The insurgents forced women to cover themselves completely under burqas, banned them from working, and restricted most education for girls.